High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) sheets are versatile materials widely used across various industries. Their durability, chemical resistance, and lightweight nature make them ideal for numerous applications. In manufacturing, HDPE sheets offer reliability for products ranging from containers to industrial components.
The construction sector also benefits greatly from HDPE sheets. They provide an effective barrier against moisture and serve as robust insulation. Yet, while HDPE sheets excel in many areas, challenges remain. For instance, their environmental impact and recyclability are subjects of ongoing debate.
In the agricultural sector, HDPE sheets play a vital role in greenhouse construction and soil stabilization. Farmers appreciate their strength and longevity. However, not everyone understands the importance of proper disposal methods. Addressing these concerns is crucial for the future of HDPE sheets in sustainable practices.
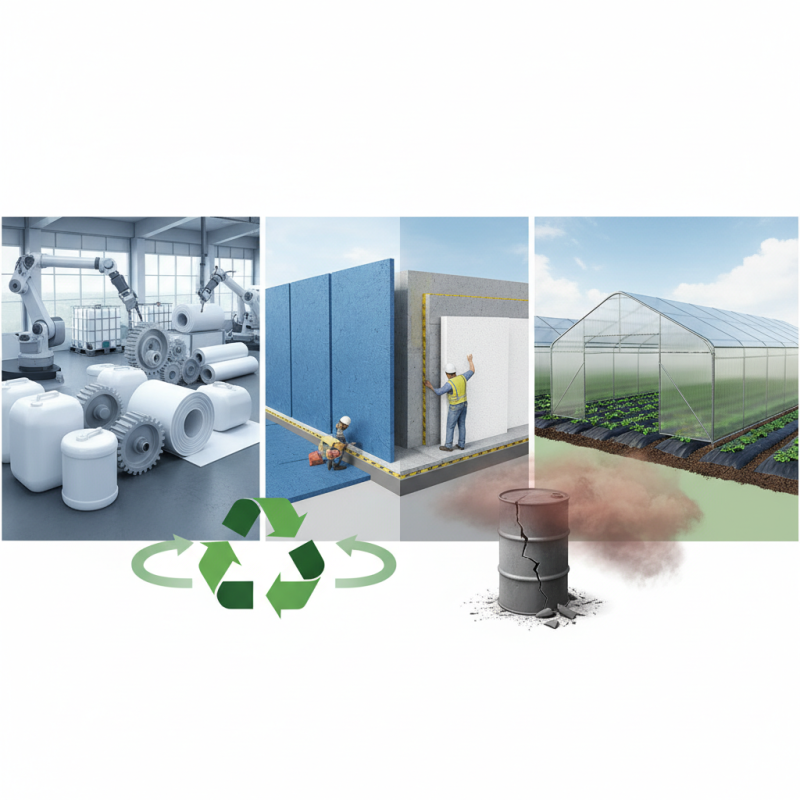


High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a widely used thermoplastic. Its unique composition makes it strong yet lightweight. Made from petroleum, HDPE consists of long chains of molecules. These chains provide the material with resistance against various chemicals and impacts.
Industries value HDPE for its durability. It's often used in packaging, construction, and even medical applications. For instance, it forms containers for household products. Yet, one must consider its environmental impact. While HDPE is recyclable, not all facilities accept it.
Understanding the composition of HDPE sheds light on its characteristics. The density allows for easy molding into various shapes. Users should remain cautious about improper disposal. More education on proper recycling techniques is necessary. This awareness can reduce plastic pollution effectively.
HDPE sheets, made from high-density polyethylene, exhibit a range of impressive properties. One notable feature is their exceptional resistance to chemicals and moisture. This makes them ideal for industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where hygiene is critical. According to a recent study by the Plastic Environmental Council, HDPE materials can withstand harsh conditions, maintaining their integrity even after prolonged exposure to various chemicals.
Another key property of HDPE sheets is their strength-to-weight ratio. They are lightweight yet incredibly durable, suitable for applications in construction and automotive industries. The American Society for Testing and Materials states that HDPE's tensile strength can reach up to 3,500 psi, making it a robust choice for many structural applications. However, this durability sometimes leads to overuse, as some industries may not fully utilize HDPE's potential, opting for substitutes that may not be as beneficial.
Moreover, HDPE sheets are highly recyclable, contributing to sustainability efforts. The recycling rate for HDPE products has seen improvements, reaching approximately 30% in some regions, as reported by the Global Recycling Foundation. While this is promising, it also raises questions about the effectiveness of current recycling systems. The need for more efficient recycling methods remains a challenge we must address.
HDPE sheets are versatile and durable. They are widely used across various industries. Their resistance to chemicals and moisture makes them a popular choice. In construction, HDPE sheets provide excellent waterproofing. They prevent water damage in structures, helping to extend the lifespan of buildings.
In the packaging industry, HDPE sheets are common. They are used for creating containers and bottles. These materials are lightweight yet strong, providing protection to products during transport. The food industry also benefits greatly from HDPE sheets, as they are safe for direct food contact, which is key for maintaining food safety standards.
Tips: Always consider the specific requirements of your industry when selecting HDPE sheets. Different grades offer various benefits. Also, invest time in understanding the thickness you need, as this can impact durability and performance. Remember that proper installation is crucial. A mistake here can lead to future issues.
HDPE sheets offer several advantages that make them a popular choice across various industries. Their durability is one of the most notable benefits. Unlike other materials, HDPE sheets are resistant to impact and wear. They can be used in high-stress environments, such as warehouses or construction sites, where durability is crucial. This resilience also means a longer lifespan, which can reduce replacement costs over time.
Additionally, HDPE sheets are non-toxic and safe for food contact. This quality makes them ideal for food processing applications. Many businesses in the food industry prefer HDPE sheets for cutting boards and countertops. Their smooth surface is easy to clean, which helps maintain hygiene standards. Furthermore, these sheets do not absorb moisture or odors, unlike materials like wood.
Some might overlook the eco-friendliness of HDPE sheets. They can be recycled and repurposed, minimizing waste. However, it's important to note that not all recycling facilities accept HDPE. This limitation can lead to waste if not managed properly. While they are cost-effective, the initial investment might deter some smaller businesses. Finding the right application can take time. Each decision requires careful consideration of the specific needs and challenges faced by a business.
HDPE sheets are popular in various industries due to their durability and resistance. However, their environmental impact is a growing concern. Recycling HDPE is critical for reducing landfill waste. According to the Plastics Industry Association, only about 30% of HDPE products are recycled in the U.S. This low rate highlights a significant gap in recycling efforts.
HDPE has numerous applications, yet its lifecycle poses challenges. While it can be recycled into new products, many consumers remain unaware of proper disposal methods. The American Chemistry Council reports that over 5 million tons of HDPE end up in landfills each year. This situation raises questions about our responsibility in managing plastic waste.
Improvements are necessary in recycling processes for HDPE sheets. Innovations in technology could enhance recycling efficiency. Moreover, educating consumers on recycling options remains essential. An increase in awareness can lead to better outcomes for our environment. The need for sustainable practices becomes clear when we examine these statistics.
| Industry | Common Uses | Recycling Rate | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Piping, Sheeting, Roofing | 30% | Low toxicity, durable, can be recycled into new products. |
| Packaging | Bottles, Containers, Bags | 27% | Recyclable, helps reduce plastic waste, minimizes landfill impact. |
| Automotive | Fuel Tanks, Bumpers, Interior Parts | 15% | Durable and lightweight, contributes to fuel efficiency. |
| Agriculture | Water Tanks, Liners, Irrigation Systems | 25% | Helps conserve water, can be reused in farming practices. |
| Medical | Surgical Trays, Tubs, Bottles | 22% | Non-reactive and hygienic, essential for safe medical applications. |