Thick plastic sheets are versatile materials used in various applications. Their durability makes them ideal for many different projects. These sheets come in different thicknesses, ensuring a variety of uses across industries.
In construction, thick plastic sheets act as barriers against moisture and dust. They provide insulation and protection for tools and materials. In agriculture, these sheets serve as effective covers for crops, protecting them from harsh weather. However, improper use can lead to issues, such as inadequate ventilation.
Home improvement projects often benefit from thick plastic sheets too. They are used to create temporary walls during renovations. These sheets help contain dust and debris, yet they sometimes fail to provide complete coverage. Users need to assess their needs carefully before proceeding. The versatility of thick plastic sheets is evident, but awareness of their limitations is essential for optimal use.
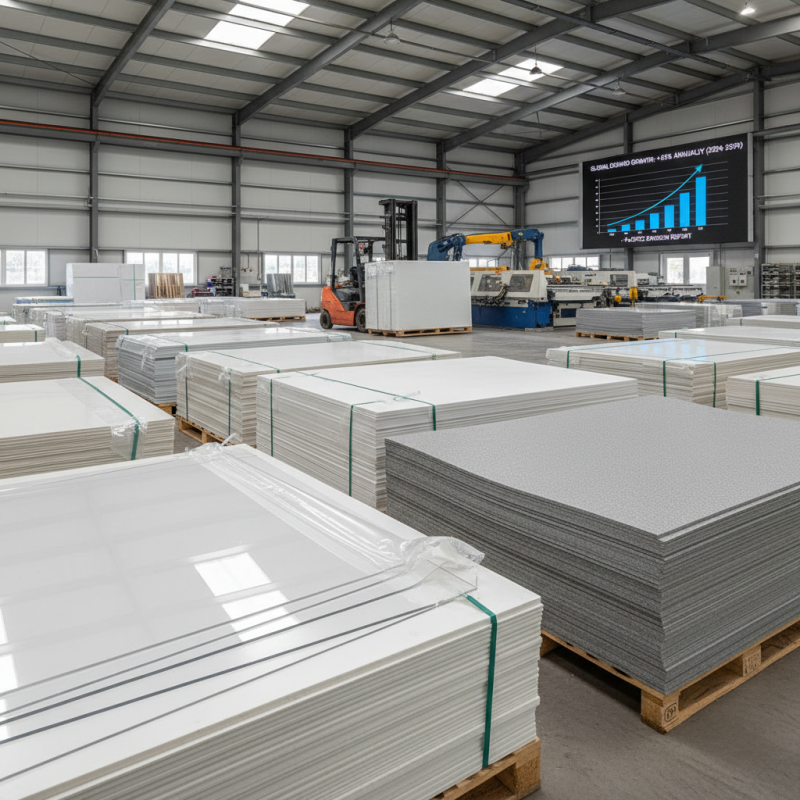


Thick plastic sheets are versatile materials used in various industries. Defined by their durability and thickness, these sheets typically range from 1 mm to 25 mm or more. Their robust nature enables them to withstand environmental factors like moisture and chemicals. A report from the Plastics Division states that the demand for thick plastic sheets is expected to grow by 4.5% annually over the next five years.
Commonly made from materials such as polycarbonate or acrylic, thick plastic sheets serve multiple purposes. They are often utilized in construction as protective barriers or safety shields. In agriculture, these sheets can function as greenhouse covers. Despite their advantages, there are concerns regarding their environmental impact. The recycling process for thick plastics is still underdeveloped, which raises questions about sustainability.
In addition, thick plastic sheets may not always meet specific user needs. For instance, while they offer strength, they can be prone to scratching and UV degradation over time. Buyers need to consider these limitations when selecting materials. There is often confusion about the appropriate thickness required for certain applications. Understanding these factors can help in making informed decisions.
Thick plastic sheets are versatile materials made from various substances. They serve different purposes across multiple industries. Common materials used in thick plastic sheets include polycarbonate, acrylic, and PVC. Each material has unique properties suited for different applications.
Polycarbonate sheets are known for their high impact resistance. They are often used in safety equipment and greenhouse construction. Acrylic sheets are lightweight and have excellent clarity. They are commonly found in signage and display cases. PVC sheets, on the other hand, are durable and moisture-resistant. They are often used in construction and manufacturing.
Tips: Consider the environment when choosing materials. Some plastics are recyclable, while others are not. Always check for local recycling options. When cutting thick plastic sheets, use the right tools to avoid fraying. A good-quality blade makes a significant difference.
It's interesting to note that not all thick plastic sheets will perform well under UV light. Some may yellow or degrade over time. This discrepancy can lead to unexpected results in long-term projects. Always do a small test before committing to larger installations or designs.
Thick plastic sheets are versatile materials used across various industries. Their thickness typically ranges from 0.25 inches to 1 inch or more. This range offers unique durability and strength. According to market reports, the demand for thick plastic sheets is expected to grow by over 5% annually. Their applications are widespread, from construction to manufacturing.
One key property of thick plastic sheets is their impact resistance. They can withstand physical stress, making them ideal for protective barriers. A study reveals that they can endure impacts that would shatter glass or weaken metal. Additionally, they are often resistant to UV light and chemicals, prolonging their lifespan in harsh environments. Such features make them increasingly popular for outdoor applications.
Ease of fabrication sets thick plastic sheets apart. They can be cut, drilled, and welded without losing integrity. However, there are limitations. Not all types provide the same clarity or aesthetic appeal. In some cases, they can warp under extreme heat. Despite these drawbacks, their affordability and effectiveness remain compelling reasons for continued use in various sectors.

Thick plastic sheets come in various forms and serve multiple purposes across different industries. They are often used in construction for temporary barriers and as protective covers. These sheets can endure weather changes, providing reliable protection. Their strength makes them suitable for flooring, especially in places that require durability.
These sheets find their applications in signs and displays too. Many businesses use them for advertising purposes. They can be easily printed on and shaped. In industrial settings, thick plastic sheets are useful for creating dividers, enhancing safety. However, they can be challenging to work with. Cutting or shaping might lead to uneven edges, requiring careful handling.
In agriculture, thick plastic sheets help to create greenhouses. They allow sunlight in but keep pests out. Farmers appreciate their versatility. Yet, improper installation can lead to air leaks, affecting plant growth. Balancing functionality and practicality is essential. It can sometimes be difficult to meet these requirements.
When selecting thick plastic sheets, clarity about purpose is crucial. These sheets have various uses, including protective barriers, signage, and construction materials. A report from MarketsandMarkets indicates that the plastic sheet market is projected to reach $10 billion by 2026, driven by demand in industrial applications.
Thick plastic sheets come in different thicknesses and materials. Consider the environment where they will be used. For outdoor applications, UV resistance is essential. In contrast, sheets for indoor use may prioritize aesthetic qualities. Selecting sheets with a thickness of at least 0.25 inches can provide durability while maintaining flexibility.
Working with thick plastic sheets requires proper tools. Cutters and saws designed for plastics reduce the risk of cracking. An industry study noted that improper handling can lead to material waste, sometimes reaching up to 20%. It's vital to measure twice before cutting. Reflecting on project goals can guide efficient material use, reducing costs and environmental impact.
| Material Type | Thickness (mm) | Common Uses | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycarbonate | 3-10 | Safety glazing, skylights, greenhouses | High impact resistance, UV protection | Can scratch easily, higher cost |
| Acrylic | 2-10 | Display cases, signage, protective screens | Lightweight, good clarity, easily machinable | Less impact resistant than polycarbonate, can yellow over time |
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | 2-12 | Construction, plumbing, signage | Economical, chemical resistant | Limited UV resistance, can warp in extreme heat |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | 3-15 | Industrial containers, outdoor furniture | Durable, resistant to impact and chemicals | Limited rigidity compared to other materials |