Industrial plastics play a crucial role in various sectors, influencing modern manufacturing and consumer products. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global industrial plastics market is projected to reach $105 billion by 2025. This growth is driven by increasing demand across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Renowned expert Dr. Jane Foster, a leading figure in material science, once stated, "Understanding the properties of industrial plastics is key to innovation." Her insight underscores the relevance of these materials in a fast-evolving landscape. From polycarbonate to Nylon, each type brings unique attributes that impact design and production processes.
Yet, the industry is not without challenges. The environmental impact of plastic waste remains a significant concern. Companies are under pressure to develop sustainable solutions. Furthermore, the diverse application of industrial plastics means that performance standards can vary. Educating stakeholders about these materials is essential to addressing both innovation and responsibility.

Polyethylene is a powerhouse in the industrial world. Its versatility is unmatched, making it essential for various applications. From packaging to construction, it plays a crucial role. When choosing polyethylene, consider its type. High-density and low-density variations each have unique properties.
Tips: Always evaluate the specific needs of your project. Different thicknesses can impact durability and flexibility.
The production of polyethylene has its challenges. It is not always environmentally friendly. Recycling options are limited, causing waste concerns. Many industries are looking for alternatives. While polyethylene is efficient, it’s not perfect.
Tips: Explore biodegradable options when feasible. Being mindful can lead to better choices for the earth.
Polyethylene’s strength is in its ease of use. It can be molded into many shapes. This adaptability helps in manufacturing components. However, it can be prone to wear over time. Regular assessments are necessary to maintain quality.
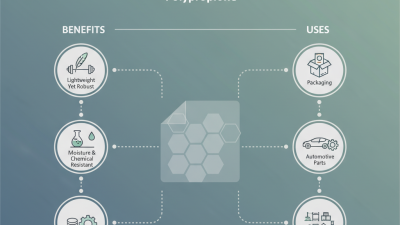
Polypropylene, known for its versatility, plays a vital role in manufacturing processes. This material is lightweight yet strong. It resists chemicals, making it ideal for various applications. From automotive to packaging, polypropylene shows great adaptability. Its ability to be molded into different shapes allows manufacturers to innovate freely.
Consider these tips when using polypropylene. Always assess the chemical compatibility with your specific environment. Experimenting with different additives can enhance its properties. It’s important to recognize that not all polypropylene grades are equal. The choice of grade can significantly impact the final product's performance.
Despite its advantages, polypropylene has limitations. It can be sensitive to UV light, leading to degradation over time. Manufacturers must carefully consider this in outdoor applications. Recycling polypropylene remains a challenge. Although it is recyclable, the infrastructure for processing it is not as robust. Always reflect on these factors when choosing materials for your projects.
This chart illustrates the common applications of various industrial plastics. Polypropylene leads the way due to its versatility in manufacturing processes.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plays a critical role in various industries. It is one of the most widely produced synthetic plastic polymers in the world. In 2020, global production reached over 40 million tons. Its versatility makes it a staple in
construction, healthcare, and automotive sectors.
PVC is favored for its durability and resistance to environmental degradation. It can withstand extreme weather conditions and UV exposure. This material is often used in pipes, siding, and medical devices. What’s notable is its cost-effectiveness. PVC can be manufactured at a lower cost compared to other materials. However, the production process and disposal methods raise environmental concerns. PVC releases harmful chemicals during incineration.
The material’s thermal stability is impressive, with a decomposition temperature around 260°C. Yet, it has limitations in high-temperature applications. As industries evolve, the push for sustainable alternatives grows. While PVC lasts long, finding eco-friendly solutions should be a priority. Balancing performance and environmental impact is an ongoing challenge for manufacturers.
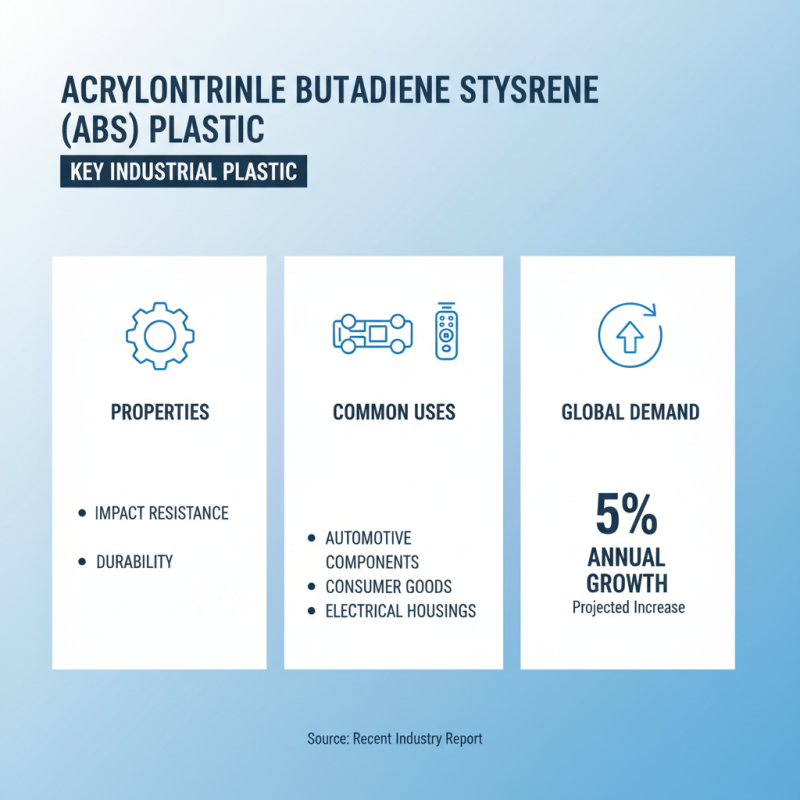
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a key industrial plastic known for its impact resistance and durability. It is widely used in automotive components, consumer goods, and electrical housings. According to a recent report, the global demand for ABS is projected to grow by 5% annually. This reflects its essential role in manufacturing.
ABS offers a balance of toughness and rigidity. Its impact resistance is notable. Studies indicate that ABS can absorb significant shock without cracking. This makes it suitable for products that endure rough handling, like toys and tools. However, its performance can vary based on environmental conditions, like temperature and humidity.
Tips: When selecting ABS for your projects, consider the specific requirements. Test its performance under expected conditions. Also, explore alternatives if extreme durability is needed. Research reveals that while ABS is effective, it may not withstand harsh chemicals. Evaluate all factors before making a decision. Make an informed choice to ensure your plastic works for your needs.

The rise of biodegradable plastics marks a significant shift in industrial practices. Companies are increasingly exploring materials that minimize environmental impact. These innovative plastics break down over time, reducing waste in landfills. Fields like packaging and automotive are leading the charge in adopting these alternatives.
Recent advancements show promise, yet challenges remain. Many biodegradable options still don't decompose efficiently in natural environments. This highlights a critical need for thorough testing and development. The complexity of blending these materials with existing supply chains can complicate their widespread use.
Despite these hurdles, the potential benefits are considerable. Biodegradable plastics can drastically reduce pollution. However, more research is essential to enhance their performance and acceptance. As industries evolve, the focus on sustainable materials may redefine product lifecycles. The journey toward greener practices continues, revealing both potential and setbacks.